http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7sZ5Nz8_cfc&feature=related
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VX1Ze5edmkE
*** take practice test 2 from Spring 2012** now we are in the middle/ meat of the course... 12:18 pm
Topic 5: Disease Establishment and Types
Symbiosis –Living together
Table 14.1
¨ Commensalism- (exists?) * one benefits, one unaffected
¨ Mutualism – both benefits (E. Coli get warmth, nutrients and protection by living in our intestines)
¨ Parasitism – One benefits, one suffers (most pathogens)
¨ Opportunism – Typically harmless until opportunity arises, then becomes parasitic (example: vaginal yeast infection... they are kept in check by acids made by bacteria, part of natural flora...if you take antibodies for strep throat, it will kill some bacteria in vagina and the yeast will grow and you will have a yeast infection, sometimes when you are pregnant you will have increased yeast infections;
example: staph. ores... most people have it on the surface on the skin, but if it goes into the internal parts of your skin it can cause diseases
example: urinary tract infection is typically caused by E. coli when you contaminate urethra opening with feces from your anus )
example picture: hermit crab in shell with anemone on shell, for many years it was categorized as commensalistic.... crab will kill and eat conch if it is not already dead and he wants the shell which would be parasitic. anemone get food from leftover that crabs eats messy. crabs scrap off anemones from old shell to new shells. Anemone helps camouflage and protect crab. so their relationship is mutualistic.
Health vs. Disease - A Balancing Act
¨ Factors of Microbe
¨levels of Virulence diagram Fig. 14.8
- ability to cause disease = virulence
- having capsules increases virulence
- toxins:
- spores
- Enzymes
- drug resistance genes
- anthrax has all the factors... very deadly
- Fig 20.8 shows antigens virulence factors
¨Dose
number of organisms acquired (dose)- typhoid (about 1 million bacteria)
- tuberculois (only one cell that finds its way into your lungs)
- salmonella (a lot to last digestive system)
- Synergy
- Presence of other organisms + or - effect (synergy)
¨ Factors of Host
– Immunocompetence / Immunocompromise
- Age (puberty is the peak of immune system, thyamus increase until puberty and then starts to descreases and replaced by fatty tissue)
- Genetic/ racial
- General health
- Nutrition (ex. Vitamin D)
- Sleep (8 hours versus 5 hours in college students, half as much Killer T cells by just not getting enough sleep for one night)
- Stress (good stress or bad, example: wedding, good job, etc, suppress production of new cells and movement of cells)
- Exercise (moderate: increase amount and movement of those white blood cells
- low sluggish
- high, ex. marathon: stress body, muscle repair, less energy given to immune system
- the balance may tip
*** http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PyorDyoabhs&feature=related
Transmission of Disease
Direct Transmission: (diseased and those they infect in same place at same time)
Touching (contact)
· Respiratory droplets Fig. 14.12
- Sexual contact
- Bites * (example direct: dog with rabies, saliva has rabies virus ; indirect: flea infects you with bubonic plague because fleas were not affected by disease;
- human bites worse because human can pass human pathogens more then other animals and typically more tissue damage)
- Feces contact? (example: Chimps fling poo at girl and got hit in the eye and got a herpes infection, lost eye. warm moist fecal material)
Indirect Transmission:
(diseased NOT in same place and time with those they infect)
· Vehicles: contaminated food, water or air (dust) (question: friend doing garden, bacteria in throat, spore formers and fungal infection, pigeon feces, mice urine dust
TB organism survives up to 2 weeks: not spitting in streets, example: legionare's disease? what was the cause? all the people who got it shopped at same grocery misters at produce section put it in the air because the water was infected.
· Fomites : inanimate objects (example: shared water bottle, shared needle, etc)
· Vectors :living organisms (not diseased) example: flea bite, flea is not sick but harbors pathogens that get human sick...
Zoonosis: Table 14.3can be direct or indirect.... (diseases of animals, example rabies.... can transfer into humans that can make us sick when they are not suppose to... flu season: cold time of year, where do they go: they live in pigs....pigs can carry human and birds flu viruses and mix both of them and then introduce the new flu virus )
- Fecal contact (dry, food, water ***NC number 2 outdoor toilets, number 1 pigs per capital) cats toxoplasmosis fecal material: cold and dry for 3 days
- can you name each vector and diseases carried? table 14.10
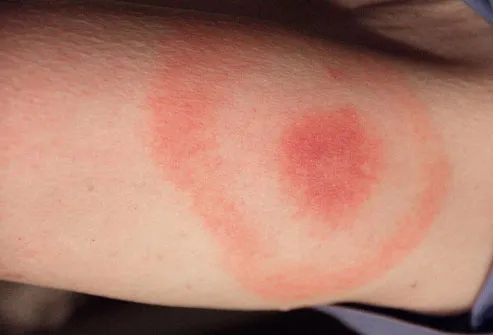
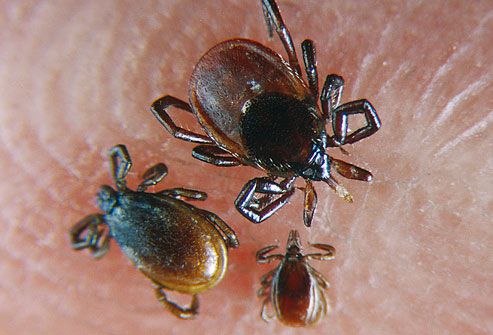
- lyme disease bull's eye
- tick: (spotted mountain fever
- pubic louse: human pubic hair (mange,
- fly (nasty because of the way they feed: they throw up digestive material and sponges up liquid. mechanical vectors... fly specks: hard round spots on window.. they can carry almost anything
- Female mosquito (malaria, west nile, dengi fever
,yellow fever) - fleas (bubonic plague, tapeworms in cats and dogs)
Reservoirs :
holds pathogen between infections (role in POPULATION)
Vectors, vehicles, and fomites can be reservoirs if pathogen survives in/on them and infects many individuals over time
Carriers: are asymptomatic infected individuals who infect many over time (all are reservoirs)
- transmitted directly or indirectly
*** drawing to help visualize....****Example: typhoid Mary private cook because she didn't wash her hands and passed it on to people... eventually worked in hospital: imprisoned to either remove her gall bladder removed or stay in prison. she refused to have surgery and remained in prison until death.... test questions will have case studies....
example: west nile virus transmission cycle: 80-90 % fatal in birds... humans are incidental hosts, mosquitoes are vectors and are reservoirs for human and birds (bounty for dead birds)
Example: flies eating a piece of steak, steak is a vehicle, flies vector to vehicle
example: respiratory droplets: direct
example: man making food without gloves...man would be a carrier which is a type of reservoir, the food is a vehicle
example: women shaking hands, if water is contaminated: water is a vehicle, immunocompromised...
The Course of Disease: 5 Stages
(Fig. 14.10)
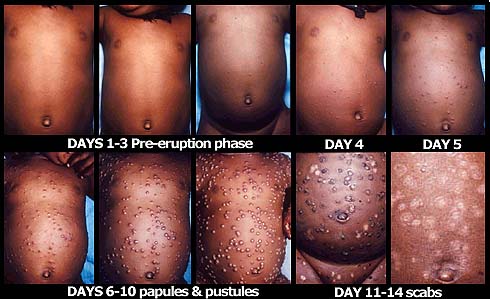
smallpox picture
8 Incubation (Table
14.9) - no symptoms : adjustment replication (bacterial infection is related to generation time of the pathogen, rabies: how close to the central nervous system)
8 Prodromal- first vague symptoms (fever, malaise (yucky feeling), lack of energy, lack of appetite, very generic etc)
8 Acute- recognizable, severe symptoms (vomiting and rash) picture of kid with measles and another picture of kid with small pox

No comments:
Post a Comment