Interferons Fig 15.7 and Table 15.4


* infected cells release
*Neighboring cells produce anti-viral proteins
* Neighboring cells protected from viral attack
*Stupid analogy? panty raids? back in the old days, before classes started... entertainment, single sex dorms, boys would grab a handful of underwear and make a pile ... 1st floor always lose underwear because they had no warning. 2nd floor would hear the screams of the 1st floor and have warning and close their doors.....the guys are the viruses and the girls are the cells being affected. the screams are like the interferons to give warning.. slammed locked door like anti-viral proteins....
*** draw picture***
(Type 1) Interferons (Fig.
15.7, Table 15.4)
Released by ____infected cell
__infected cell_______ cells produce
_______antiviral proteins___________ (AVP)
Neighboring cells protected from ____viral attack________
Complement Activation (Fig. 15.8, 15.9)

Complement proteins are found separately ___in blood_____________
Alternate
pathway: triggered to ___bind sequentially__________ by ______________________
So only works against
____pathogen molecules (gr - wall capsule)_____ in level 2 defense
(classic pathway in level 3 affects more types of pathogens)
Cause/enhance
1- Phagocytosis (opsomization) (enhanced phagocytosis better, makes it eat it better by making surface sticky)
2- Inflammation (without having to have cell damage first... deliver more phagocytes, natural killer cell: bacteria and larger eukaryotic cells)
(15.10)
3- Membrane Attack Complex:
* Combined complement proteins form a channel
* cell contents leak out (lysis):
(lots of holes not just one)


* Combined complement proteins form a channel
* cell contents leak out (lysis):
(lots of holes not just one)

(15.9, 15.11)


Topic 7b: Level Three
Defenses
Cell-Mediated Immunity
and
Humoral Immunity


Where are we?
Level one takes place __at the surfaces_________________
Level two occurs mainly ___just beneath your surfaces_________________
Level three is __systemic (throughout the body)_____________

Level 3 Defenses: Fig. 16.2
Command center = ____lymphoid organs_____________
___monitor body fluids
* Lymphatic system - series of blind ended vessels which drain body tissues: punctuated by lymph nodes
* Lymphatic system - series of blind ended vessels which drain body tissues: punctuated by lymph nodes
Cells involved are __T_lymphocytes_________and _____B lymphocytes___________, both
produced in the __stem cell______(we make T and B cells against every antigens on the face of the earth and we destroy the ones that would attack you, or your own cells because they have antigens on those cells... autoimmune disease is when the maturation step doesn't happen and they attack your own cells)
But ___T lymphocytes____________mature in the
___thymus________________ (Fig. 16.8)
While ___B lymphocytes______ mature in the
_____bone marrow______________ (Fig. 16.9)
T and B Cells both
colonize the same lymphatic tissues: ***lymph nodes,
***spleen (recycle red blood cells, septicemia or infection that has APC that is monitored by the spleen: monitors fluid in the blood)
***spleen (recycle red blood cells, septicemia or infection that has APC that is monitored by the spleen: monitors fluid in the blood)
***Mucosal Associated Lymphatic Tissue
(MALT):
* tonsils
* Adenoids
* Peyer's patches (in small intestines)
* Appendix (corner large intestines)


* tonsils
* Adenoids
* Peyer's patches (in small intestines)
* Appendix (corner large intestines)


(Remember) Level 2 Sets the Stage for Level 3:
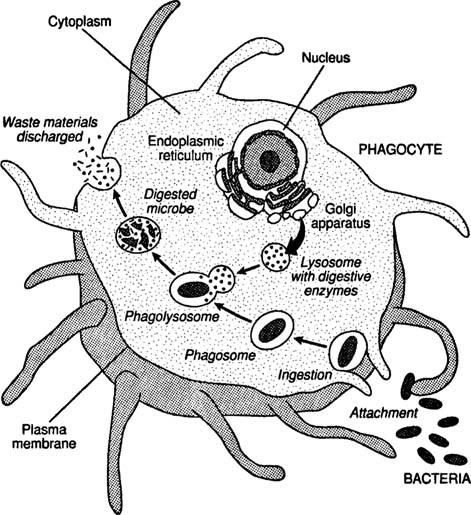
* Phagocytosis - Antigen processed and placed on phagocytic cell surface.

* Phagocytosis - Antigen processed and placed on phagocytic cell surface.
Processing of antigen in process of
_________________________
MHC- major histocompatibility complex = "holder"
APC = antigen presenting cell
Class
I MHC: Fig. 16.10a, 16.12
Found on: all nucleated cells (tells you what is inside those cells, most it will be empty but if it is abnormal, it will put proteins in the MHC and tell the body its abnormal)
*** Display for: self recognition
***** ID of abnormal cells
***** ID of abnormal cells
Used
for: signaling if normal or abnormal
Class
II MHC: Fig. 16.10b, 16.13
Found
on: cell membrane of
- macrophages
- dendritic cells
- B lymphocytes
Used
for: APC presents antigen to immune cells


Overall general summary of the two branches of specific defense: (PRINT OUT and complete Level 3 Defenses Chart)
Level 3 Defenses of the body
Process
|
Cells involved
|
Activated by?
|
What leaves lymph node?
|
Action / Effect
|
Cell-Mediated
|
T cell
|
|||
Humoral
|
1-
2-
3-
4-
a)
b)
c)
5-
|
Size comparison of antigens/pathogens: Tell what response
would be effective against each.
Tiny
(too small to phagocytize)
|
Small
|
Large
(too big to phagocytize)
|
|
Examples
|
|||
Cell mediated
|
|||
Humoral (specific)
|
Cell-Mediated
Immunity
- First initiated (1-2 days)
- T-cell activation and cloning
- Specific cytotoxic T-cells go throughout body
Humoral Immunity
- Delayed initiation (2-5 days)
- B cell activation and cloning to plasma cells
- Plasma cells release antibodies
- Antibodies go throughout body
Detailed
description of Cell-Mediated Immunity: Fig. 16.14
APC go to lymph node and: antigen on cell surface (in MHC II)
* APC touches and activates naive T helper cells. (Th0)
* T cell receptor: membrane protein matches MHC II on APC)
*********CD4 affected by AIDS

* APC touches and activates naive T helper cells. (Th0)
* T cell receptor: membrane protein matches MHC II on APC)
*********CD4 affected by AIDS

* activated Th0 cells create Th1)
* Th1 secrete cytokines (signal chemicals)
*Th1 cytokines stimulate
1. APC cells - kill better faster
2. Naive T cytotoxic cells (Tc0)
* activated Tc0 clone rapidly (all clones have info. about antigen).
- Majority: Tc clones - active now
- Minority: T memory (Tm) clones - active only later
* Cloned cytotoxic T cells go to bloodstream and tissues. (chemotaxis - find antigen on cell surfaces)
* Tm cells remain dormant (wander through tissue)
* Th1 cells remain in lymph node to continue cell activation
*Tc cells use chemotaxis - find antigen in MHC - 1
* use perforin and granzyme to destroy specific abnormal eukaryotic cells (by MHC - 1)
* Fig 16.15


*** stop and draw this process*** one drawing of both.....

************* she drew a picture of pathogen entering the body via a cut. the pathogen eaten by a phagocyte which became a APC and went to the lymph node. the naive Th0 or T helper cell was activated. Cytosine activated ..... also Th1 some is activated which leave lymph node into the tissue and it kills infected self cell with Tc (similar to killer cells but is for a specific antigens), the rest are memory Th1 ****

When the threat is over....
* cloned Tc cells and Th1 cells die (short lived) (have automatic apoptosis programed cell death)
* memory T cells (Tm) live forever (?)
* Second exposure to same antigen
* all primary responses at normal time
* Tm cells: no need for APC
- convert to active Tc cells within minutes
- specific cell killing

Study Tips: Just some ideas I found useful:
- Take good notes and review them every night for at least 15 minutes when you get home to see if you understand the material. Ask the professor questions if you find something confusing. She's really good about returning emails.
- Find a partner to quiz you by asking you questions that might be on the test (use the practice test and other worksheets for ideas).
- Take a blank lecture outline and see if you can fill it out by memory
- Try drawing and labeling the diagrams and processes the professor had us draw from memory
- Vocabulary, vocabulary, vocabulary:LEARN IT! Most of the key ones can be found on the lecture outline.
- Try to attend the online review session on Blackboard: Sunday 8-9 pm. I found it very helpful.
- Make sure to get some sleep the night before and eat a good breakfast.
No comments:
Post a Comment