not sure how much I'll get with just one hand but I'll give it a go:
x ray of my hand, you can see the dislocation of the ulna upward from the normal position
Review:
group work: 5 top ways (activities) to get HIV
group work: 5 top ways (activities) to get HIV
Why HIV/AIDS is unusual:
Why no vaccine:
-HIV evolves rapidly (many strains and types)
-Ethical testing of vaccine?
-HIV evolves rapidly (many strains and types)
-Ethical testing of vaccine?
Transmission depends upon many
factors:
- viral load of the body fluids varies
- body fluid has cells?
- case of entry of virus into bloodstream
* trauma (rape, or anal)
* presence of other sexually transmitted diseases
- viral load of the body fluids varies
- body fluid has cells?
- case of entry of virus into bloodstream
* trauma (rape, or anal)
* presence of other sexually transmitted diseases
Transmission of HIV
********(Ranked in order of likelihood of infection) group work question********
1. blood or blood products introduced IV
* blood transfusion with contaminated blood (untested)
* contaminated clotting factor
* IV drug users: needle sharing
1b miscellaneous blood or body fluid exchange
2. perinatal (placental or during birth)
3. rape/ anal intercourse as receiving partner
4. vaginal intercourse as receiving partner
5. sexual intercourse as donating partner or oral sex
********(Ranked in order of likelihood of infection) group work question********
1. blood or blood products introduced IV
* blood transfusion with contaminated blood (untested)
* contaminated clotting factor
* IV drug users: needle sharing
1b miscellaneous blood or body fluid exchange
2. perinatal (placental or during birth)
3. rape/ anal intercourse as receiving partner
4. vaginal intercourse as receiving partner
5. sexual intercourse as donating partner or oral sex
Topic 8b: Influenza
*old flu, bird flu, swine flu
pic: kid kiss pig
pic: kid kiss pig
Influenza viruses
Type A: world wide pandemics, infect all mammals and birds
Type B:small epidemics in vulnerable populations, infect mammals only
Type C:infect mammals only, rarely causes disease in humans
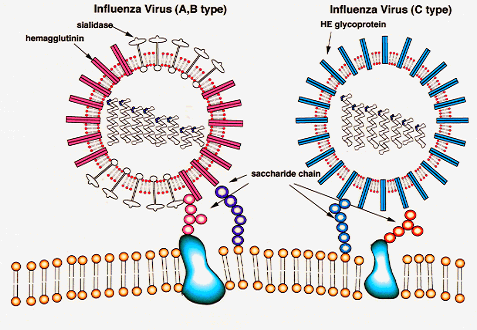
Structure of Type A
(Box. p. 736)
Genome: RNA virus : 8 strands/ inside capsids
Enveloped
with matrix protiens: ion channel M2
Two important peplomer types:
Hemagglutinin
Function:host cell binding
Blocked
by drugs: amantidine/ rimantidine (blocks uncoating)
Neuraminidase
Function: helps release progeny
Blocked
by drugs: Tamiflu & Relenza (only these 2 drugs work on swine flu and bird flu)

Why do you need a new shot every year?
The viruses change!
*body recognizes virus by anatomical parts (antigen)
HA –hemagglutinin antigen
NA –neuraminidase antigen
We identify flu viral types
by:
* numbering antigens
*location/date first isolated in humans
*location/date first isolated in humans
sleeve from flu shot: split virion inactive ultra violet, centrifug.....
Flu “shot” is: soluble subunit
Flu-mist vaccine is: live attenuated virus
list if year by year flu shot
3 Viral types seen in annual
seasonal vaccines are:
*Two type A (H1N1 and H3N2) and one type B
*high rate of genetic (thus antigenic) change within & between flu seasons
*vaccine is a cocktail of international influenza committee's best guess for this year's strains
*Two type A (H1N1 and H3N2) and one type B
*high rate of genetic (thus antigenic) change within & between flu seasons
*vaccine is a cocktail of international influenza committee's best guess for this year's strains
Two means of
genetic change in flu viruses: Fig. 25.38
Antigenic Drift
* tiny mutations introduce small antigenic changes (RNA virus more mutations)
* gradual changes in viruses over time
fig 25.38
* gradual changes in viruses over time
fig 25.38
Antigenic Shift
(reassortment)
*2 flu viruses infect same host cell
*New viral hemagglutinin (or less commonly, neuraminidase) in existing viruses

*2 flu viruses infect same host cell
*New viral hemagglutinin (or less commonly, neuraminidase) in existing viruses

*****break*****
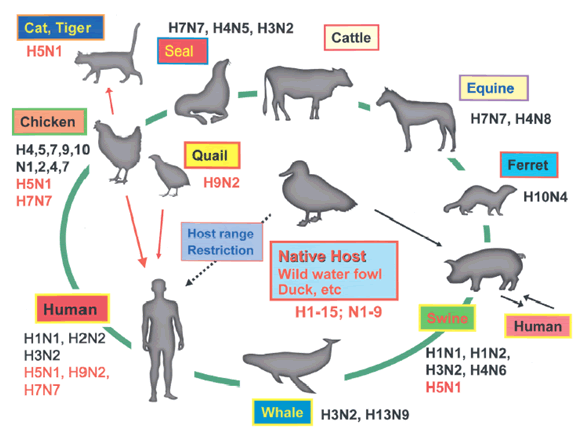
Connections between human /
pig / bird flu viruses:
* humans and pigs can share viruses
* pigs and birds can share viruses
* humans normally can't get it directly from birds
*pigs are mixing pot where human, pig, and bird virus can co-infect same cell
* pigs and birds can share viruses
* humans normally can't get it directly from birds
*pigs are mixing pot where human, pig, and bird virus can co-infect same cell
*****draw this?***draw human cell and human flu and able to match receptor proteins and infect cell....pigs and humans both have human and pig flu receptors..wild card birds....share with pigs not human*****


* non human flu viruses are very different from human viruses(all 8 RNA strands and all
Why is the new H5N1 bird flu virus of concern?
highly lethal/ virulent: rare human cases of bird flu are often lethal
* (but so far. poorly passed from person to person): mutation needed to be pandemic
* (but so far. poorly passed from person to person): mutation needed to be pandemic
Why is the new H1N1 swine flu virus of concern?
* is moderately virulent in US
* return highly virulent like 1918-1919 "Spanish flu"* Easily passed from person to person
Where do flu viruses live between epidemics?
* probably reservior animals
* migratory or domestic birds
* probably reservior animals
* migratory or domestic birds
*****group activity*****
*does this image antigenic drift or shift? define both . why

No comments:
Post a Comment