Level 1 reveiw:

Process: * Cell membrane engulfs foreign or particulate material
* Engulfed material is digested or secreted



http://www.conkwest.com/natural-killer-cells
short life span: flux with immunocomptence
*** group activity 9: how do you think APC cells form to carry viral antigens to start level 3 defenses?
*viruses too small for phagocytosis!
couple of ways to do it....
1. the virus attach and pentrate your cell..... enter cell and has markers on surface that says its infected (has antigens that says its abnormal)..... carry out viral life cycle.... cell lyse ... phagocytic cell eats pieces
2. virus enters has markers on surface... natural killer cell triggers apoptosis and triggers apoptosis and phagocytic cell eats and becomes a APC.
*******

Other Level 1 Defenses (table 15.2)
·
Urinary tract
o
Flushing – urine
·
Genital tract (females)
o
pH low
o
ciliary escalator
o
normal flora (yeast, bacteria, etc)
·
Digestive tract
o
(stomach, intesines) Peristalsis/flushing
o
(fiber = cellulose, undigestive by humans but
helps scrap and clean off walls of intesines…. Make cake, rubber spatula, fiber
like spatula that takes bacteria out of digestive tract)
* Stomach Acid
* Digestive enzymes
* Normal Flora (intestines)
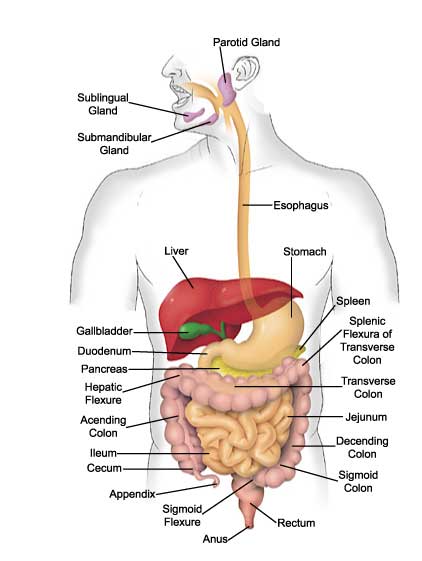
**** you should now be able to fill out the entire Level 1 defenses comparison chart.****

**** you should now be able to fill out the entire Level 1 defenses comparison chart.****
Level Two and Three Defenses:
Key Players are White Blood Cells (Fig. 15.4, Fig. 15.5)
Key Players are White Blood Cells (Fig. 15.4, Fig. 15.5)
*** what we are looking at is what happens after the pathogens get past the first layer of defense**
**review anatomy and physiology: blood cells and blood cell types, stem cells found in bone marrow... diagram explained:
**review anatomy and physiology: blood cells and blood cell types, stem cells found in bone marrow... diagram explained:
Natural Killer cell is not from the same line as from the ones above but they are important because they will come and kill....will look at progranulocyte types that control inflammation: Basophil, eosinophil, neutrophil
Level 3: T lymphocytes B lymphocytes

****make sure to say they are WHITE BLOOD CELLS on test ***
Level 3: T lymphocytes B lymphocytes

****make sure to say they are WHITE BLOOD CELLS on test ***
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Level Two Defenses: (PRINT OUT and complete Level 2 Defenses Chart)
Phagocytosis (Fig. 15.6)
Phagocytosis (Fig. 15.6)
Process: * Cell membrane engulfs foreign or particulate material
* Engulfed material is digested or secreted

* what kind of cells carry out phagocytosis?

- Neutrophiles (bloodsteam and tissues)
- Monocytes (bloodstream ONLY)

- Macrophages - derived from monocytes (tissues only)
- dendritic cells (fig 16.11) have long thin processes that stick out
- Kupffer cells stay in liver rest of life span
- Microglial cells (in brain)

Steps in Process of Phagocytosis
Ø White blood
cells find bacteria by process of _____taxis_____________________
Ø Lysosomes
(pouch of lysozyme, acids (ex. HCl), Superoxide, digestive enzymes) in cell cytoplasm
Ø Pseudopods
surround and ingest particulate material into pouch (______phagosome______)
Fig. 15. 6
Ø Fusion of
___phagosome___ + ___lysosome____ = ____phagolysosome_____
Ø digest
material, move to surface to eject undigested
Works best against: bacteria, small yeast, fragments of dead self cells
*** shows website that shows size between virus and phagosome because its too small to be grabbed unless clumped into a big wad****
*** draw picture***reminds about level 2 chart**
*** break****
*** draw picture***reminds about level 2 chart**
*** break****
Setting the Stage for Level 3:
After phagocytosis –
Antigen (unique, recognizable parts of pathogen) processed and placed on phagocytic cell surface
MHC – major histocompatibility
complex (called that because they are imbedded in cell membrane, first discovered for tissue typing for transplants: "histo" tissue) = "holder" recognizable pieces on the surface


Phagocytic cell is now an
_Antigen presenting cell__ (APC)
(Fig. 16.13)


What are
examples of antigens? (Fig. 16.3)
* Usually parts of proteins (complex)
Bacterial antigens:
Bacterial antigens:
- cell wall or membranes
- exoenxymes or exotoxins
- flagellar, pili or fimbrae
- capsule or glycocalyx
Viral antigens
- capsomeres
- peplomers
- enzymes
Fungal/Protozoal/Worm
- cell surface proteins
Abnormal “__self__” cells": also have antigenic proteins on surfaces
Inflammation


Damage to cells (basophiles and mast cells): (15.14)
Causes release of *Histamine, prostoglandins, leukotreines*: (Fig.
15.11)
These chemicals cause 2 changes:
Increased__arteriole dilation____


Increased ____capillary permeability_________
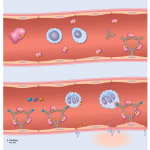

-blood leaves vessels: diapedesis
-Level 2 cells increase in tissue
Resulting signs of inflammation:
- rubor = redness
- calor = heat
- tumor = swelling
- dolor = pain
Overall Result: MORE White blood cell activity in that local area
Natural killer cells


Cells are a type of: wandering WBC (lymphocyte)
use ___perforin (make pore)___ and _granzyme(trigger apoptosis)__ to kill
__abnormal EUKARYOTIC__ cells
_____perforin__________ creates pore in cell
_____granzyme_________ triggers apoptosis enzymes in cell
(eukaryotes only)
Best defense against: infected self cells, cancerous cells, Yeast or protozoa (cells too large to phagocytize)
(___Phagocytes___ eat dead cell fragments)
**picture apoptosis cell cancer cell, NKC ***


**picture apoptosis cell cancer cell, NKC ***


http://www.conkwest.com/natural-killer-cells
short life span: flux with immunocomptence
*** group activity 9: how do you think APC cells form to carry viral antigens to start level 3 defenses?
*viruses too small for phagocytosis!
couple of ways to do it....
1. the virus attach and pentrate your cell..... enter cell and has markers on surface that says its infected (has antigens that says its abnormal)..... carry out viral life cycle.... cell lyse ... phagocytic cell eats pieces
2. virus enters has markers on surface... natural killer cell triggers apoptosis and triggers apoptosis and phagocytic cell eats and becomes a APC.
*******

No comments:
Post a Comment